04. Bacteria
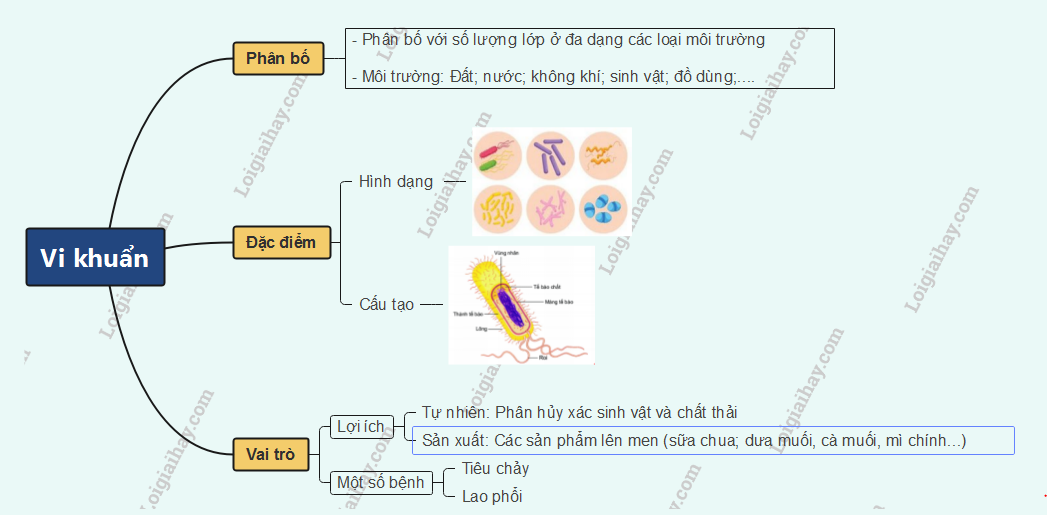
I. Bacterial Diversity
* Bacteria are microscopic organisms, only visible with a microscope.
* Habitats: Found in air, water, soil, within our bodies, and other living organisms.
* Shapes: Vary greatly in shape, occurring individually or in clusters. Three typical forms include rod-shaped, spiral-shaped, and spherical.
II. Bacterial Structure
* Bacteria have a unicellular structure consisting of main components: cell membrane, cytoplasm, and a nucleoid region containing genetic material.
* Most bacteria have a cell wall surrounding the cell membrane.
* Some bacteria possess flagella for movement and pili (or fimbriae) to attach to host cells.
III. Role of Bacteria
* Most bacteria are beneficial and play a very important role for humans and all life on Earth.
* Role in Nature:
* Nitrogen-fixing bacteria.
* Bacteria decompose dead organisms and animal waste into nutrients.
* Role in the Human Body:
* Beneficial bacteria in large numbers inhibit harmful bacteria, protect the skin, and enhance immunity.
* Aid in digestion.
* In Practical Life: Bacteria are used in food processing, antibiotic production, pesticide production, waste treatment, etc.
IV. Some Diseases Caused by Bacteria
* Bacteria cause many dangerous diseases in humans:
* Cholera: Caused by Vibrio cholerae. Symptoms include diarrhea, vomiting, high fever. Transmitted through contaminated food and water.
* Skin Infections: Caused by Staphylococcus aureus. Bacteria invade damaged skin areas causing redness and swelling. Easily spread through direct or indirect contact with contaminated objects.
* Pulmonary Tuberculosis (TB): Caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis invading the lungs. Symptoms include prolonged cough, fever, fatigue. Easily spread through respiratory droplets via close contact with infected individuals.
* Antibiotics are used to treat bacterial diseases. However, indiscriminate use of antibiotics without a doctor's prescription leads to drug resistance, making treatment difficult.
* Bacteria also cause diseases in plants and animals:
* Bacterial wilt in tomatoes and potatoes.
* Fowl cholera in poultry and livestock.
* Swine erysipelas in pigs.
* Bacteria cause spoilage of food and beverages.
Background Colour
Font Face
Font Kerning
Font Size
Image Visibility
Letter Spacing
Line Height
Link Highlight
Text Colour